摩尔定律下的挑战:
晶体管大小限制
电泄露
散热
Memory Type
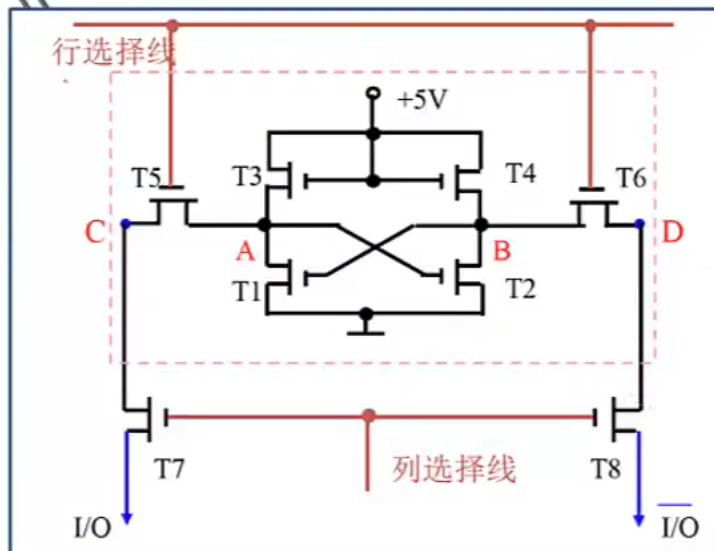
RAM(random access memory): DRAM(dynamic), S(static)RAM
ROM(read only memory): ROM, P(programmable)ROM, E(erasable)PROM, E(electrical)EPROM, FLASH EPROM (USB)
EDO(extended data out) DRAM
S(synchronous)DRAM
DDR(double data rate SDRAM)
CPU的指令集:Intel X86, ARM
汇编语言--assembly language
小结:
程序必须要经过编译才能转换成CPU所能接受的指令;
一句程序有可能转换为多句指令;
在控制器的协调下连续、依次执行相应的指令;
程序执行过程是在内存中完成的;
程序在执行过程中,在内存中的不同区域,存放代码和相关的数据;
EX1:
// Example program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 0, y = 0, z = 0, t1 = 0, t2 = 0;
while (x < 34) {
while (y < 51) {
while (z < 101) {
t1 = x + y + z;
t2 = 2 * x + 4 * y + z;
if (t1 == 100 && t2 == 200) {
cout << x << " " << y << " " << z << endl;
}
z++;
}
y++;
}
x++; } return 0; }
EX2:
// Example program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int items[10]={4,2,7,1,6,9,5,3,8,3};
int tmp=0;
for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){
cout<<items[i]<<" ";
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
for(int j = i; j<10;j++){
if(items[i]<items[j]){
tmp = items[i];
items[i]=items[j];
items[j]=tmp;
}
}
}
cout<<endl;
for(int i = 0; i<10;i++){
cout<<items[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
学习一门程序设计语言
数据成分:有哪些数据类型?如何使用?
运算成分:有哪些运算符号?如何使用?
控制成分:三种类型的控制语句是如何写的?
传输成分:在程序中如何输入和输出数据?
// Example program
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout<<"sizeof(short int)="<<sizeof(short int)<<endl;
cout<<"sizeof(int)="<<sizeof(int)<<endl;
cout<<"sizeof(long int)="<<sizeof(long int)<<endl;
return 0;
}
赋值运算总结:
两边类型不用:自动完成类型转换
常数赋给短数:截取长数的低位送给短数
短数赋给长数:保持不变
符号位的赋值处理:直接赋值,不管符号位还是数字位
定义数组的长度
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 4
int main() {
int a[N] = { 1,2,3,4 };
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
允许定义:
int a[] = {1,2,3,4};
都一样:
int a[4] = {0};
— — — — — — — — —
cout << setw(3) <<a[i][j]; //输出占三个字符位
— — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int sum = 0, a[100] = { 0 };
for (int i = 2; i < sqrt(100.0); i++) {
sum = i;
if (a[sum] == 0) {
while (sum < 100) {
sum = sum + i;
if (sum < 100)a[sum] = 1;
}
}
}
for (int i = 2; i < 100; i++) {
if (a[i] == 0)cout << i << " ";
}
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a;
while(cin>>a)
cout << a;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a;
while((a = cin.get())!=EOF)
cout << a;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a;
while(cin.get(a))
cout << a;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char c;
while(c = getchar())
cout << c;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[10] = "Computer";
cout << a;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[2][2] = {"aa","bb","cc","dd"};
for(int i =0; i < 7; i++)
cout << a[i] <<endl;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[10];
while(cin>>str)
cout << str <<endl;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char ch[20];
cin.get(ch,10,'o');
cout << ch << endl;
return 0;
}
— — — — — — — — — —
#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char ch[20];
cin.getline(ch,10,'o');
cout << ch << endl;
return 0;
}

#include <iostream> using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a[10][10];
int n = 0;
cin >> n;
cin.get(); //read n first
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin.getline(a[i],10);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << a[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
No comments:
Post a Comment